2.3.2 Choosing the waveform – WAVE knob
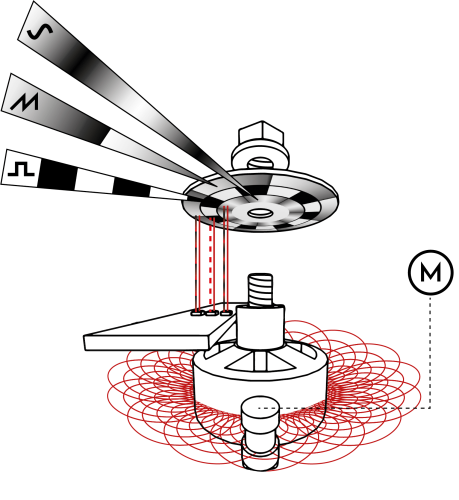
Turn the WAVE rotary switch to select one of the four Waveforms [WAVE] available for each of the MOTOR Synth’s motor VOICES: Optical Sine “OPT SINE”, Optical Triangle “OPT SAW”, Optical Square “OPT SQ” and Motor electromagnetic inductive “M”.
Tip 1: The main PLAY SCREEN provides an oscilloscope for the final output waveform. To monitor the waveform of a single motor, play one note and turn the MASTER VOLUME to max. Then set the VOLUME of other voices to 0 and set the FILTER TYPE to ALL PASS with the DRIVE and RESONANCE knobs set to minimum.
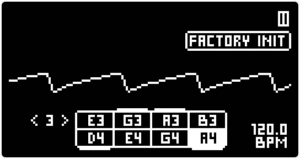
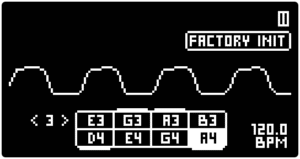
Tip 2: Since the nature of the instrument does not allow for waveshaping before the FILTER, it may be a good idea to set both MOTOR VOICES to the same SCALE. This will allow for mixing different WAVESHAPES and AMP ENVELOPES to create different waveforms.